 Request a FREE Sample of our FcRn Binding Kit!
Request a FREE Sample of our FcRn Binding Kit! Request a FREE Sample of our Fc gamma RI / CD64 Binding Kit !
Request a FREE Sample of our Fc gamma RI / CD64 Binding Kit !
 Happy Holiday! Limited Keychain here with your next order
Happy Holiday! Limited Keychain here with your next order Happy Holiday! Limited Keychain here with your next order
Happy Holiday! Limited Keychain here with your next order
 Request a FREE sample of our GMP products!
Request a FREE sample of our GMP products!  Request a FREE sample of our GMP products!
Request a FREE sample of our GMP products!
> Anti-idiotypic Antibodies An idiotope is the unique set of antigenic determinants (epitopes) of the variable portion of an antibody. An anti-idiotypic (Anti-ID) antibody binds to the idiotope of another antibody, usually an antibody drug, which makes it a very powerful tool for antibody drug development, especially for immunogenicity and PK/PD analysis.
To support preclinical/clinical immunogenicity and PK analysis, ACROBiosystems has developed a series of high-affinity anti-idiotypic antibodies. Our pipeline covers five hot targets including adalim*mab, Ritux*mab, Cetux*mab, Trastuz*mab, and Bevaciz*mab. To help the drug development process, we provide assay protocols which can be applied to different application scenarios.
| Molecule | Cat. No. | Antigen | Neutralizing Activity | Application |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Adalimu*ab | ADB-Y19 | Anti-Adalimu*ab Antibodies (AY19) | Neutralizing Antibody | ADA assay; Neutralizing assay; Indirect ELISA |
| Bevacizu*ab | BEB-Y10 | Anti-Bevacizu*ab Antibodies (AY10) (MALS verified, recommended for PK/PD) | Neutralizing Antibody | PK bridging ELISA; Neutralizing assay; Indirect ELISA |
| Bevacizu*ab | BEB-Y12 | Anti-Bevacizu*ab Antibodies (AY12) (recommended for neutralizing assay) | Neutralizing Antibody | ADA assay; Neutralizing assay; Indirect ELISA |
| Bevacizu*ab | BEB-Y9 | Anti-Bevacizu*ab Antibodies (AY9) (recommended for ADA assay) | Neutralizing Antibody | ADA assay; Neutralizing assay; Indirect ELISA |
| Bevacizu*ab | BEB-BY13 | Biotinylated Anti-Bevacizu*ab Antibodies (AY13) (recommended for PK/PD) | Neutralizing Antibody | PK bridging ELISA;Neutralizing assay; Indirect ELISA |
| Cetuxi*ab | CEB-Y27 | Anti-Cetuxi*ab Antibodies (AY27) (recommended for ADA assay) | Neutralizing Antibody | ADA assay; Neutralizing assay; Indirect ELISA |
| Cetuxi*ab | CEB-Y31 | Anti-Cetuxi*ab Antibodies (AY31) (Non-Neutralizing) | Non-Neutralizing Antibody | ADA assay; Indirect ELISA |
| Cetuxi*ab | CEB-Y28 | Anti-Cetuxi*ab Antibodies (AY28) | Neutralizing Antibody | ADA assay; Neutralizing assay; Indirect ELISA |
| Cetuxi*ab | CEB-BY31 | Biotinylated Anti-Cetuxi*ab Antibodies (AY31) (recommended for PK/PD) | Non-Neutralizing Antibody | PK bridging ELISA; Indirect ELISA |
| Rituxi*ab | RIB-Y36 | Anti-Rituxi*ab Antibodies (AY36) (recommended for ADA assay) | Neutralizing Antibody | ADA assay;Neutralizing assay; Indirect ELISA |
| Rituxi*ab | RIB-Y37 | Anti-Rituxi*ab Antibodies (AY37) (recommended for PK/PD) | Neutralizing Antibody | PK bridging ELISA;Neutralizing assay;Indirect ELISA |
| Rituxi*ab | RIB-FY35c | FITC-Labeled Anti-Rituxi*ab Antibodies, Mouse IgG1 | Neutralizing Antibody | ADA assay;Neutralizing assay; Indirect ELISA |
| Trastuzu*ab | TRB-Y5b | Anti-Trastuzu*ab Antibodies (AY5b) (recommended for PK/PD) | Non-Neutralizing Antibody | Neutralizing Antibody |
| Trastuzu*ab | TRB-Y1b | Anti-Trastuzu*ab Antibodies (AY1b) (recommended for PK/PD) | Neutralizing Antibody | PK bridging ELISA; Neutralizing assay; Indirect ELISA |
Therapeutic proteins such as monoclonal antibodies are currently essential in the treatment of cancer, autoimmune disease, and other diseases. Since protein has its intrinsic feature of immunogenicity owing to its structure containing potential B-cell and T-cell epitopes, therapeutic proteins have the potential to induce Anti-Drug Antibodies(ADA) even if the protein has the same amino acid sequence as endogenous human proteins. The emergence of ADA in patients can potentially lead to loss of efficacy and/or adverse events. Therefore, immunogenicity risk assessment and risk-mitigating strategies are required during the development of therapeutic protein products.
Developing a mono/multi-clonal antibody in-house as a positive control for ADA assay is extremely time-consuming. To solve this problem, ACROBiosystems developed a series of anti-drug antibody standards for ADA assays.
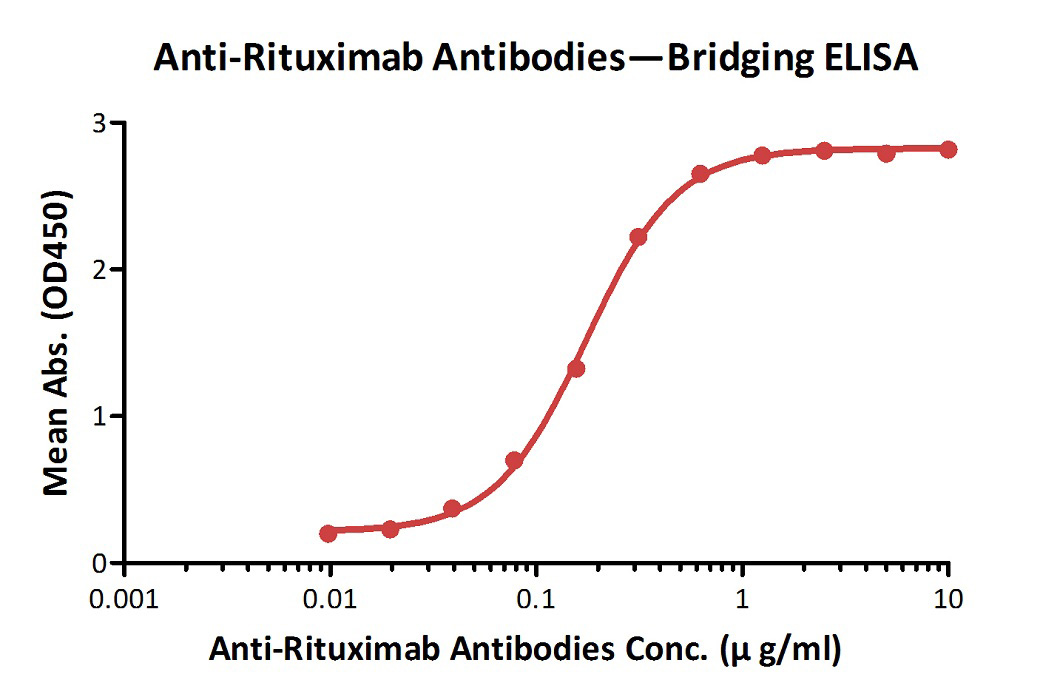
Anti-Ritux*mab Antibodies bridging ELISA for Anti-Drug Antibody (ADA) assay development. Immobilized Ritux*mab at 1 µg/ml, added increasing concentrations of Anti-Ritux*mab Antibodies (Cat. No. RIB-Y36, 10% human serum) and then added biotinylated Ritux*mab at 2 µg/ml. Detection was performed using HRP-conjugated streptavidin with a sensitivity of 9.7 ng/mL.
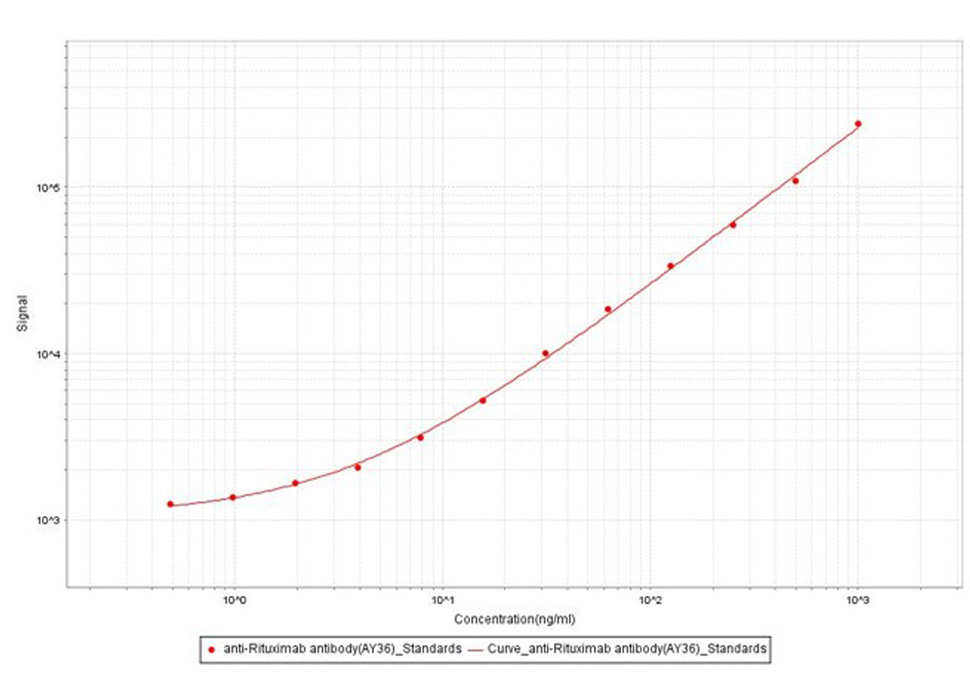
Anti-Ritux*mab Antibodies bridging MSD for Anti-Drug Antibody (ADA) assay development. Added the mix solution (biotinylated Ritux*mab at 5 µg/mL, SULFO-Ritux*mab at 5Nµg/mL and increasing concentrations of Anti-Ritux*mab Antibodies (Cat. No. RIB-Y36, 100% human serum). Detection was performed using MSD Assay with a sensitivity of 0.97 ng/mL.
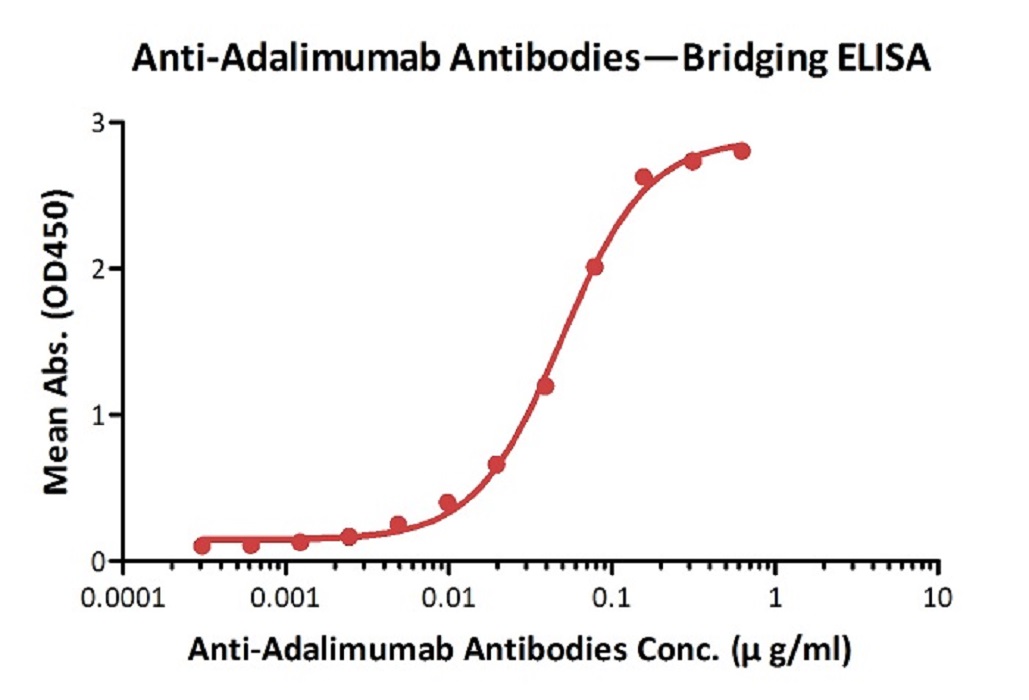
Anti-Adalim*mab Antibodies bridging ELISA for Anti-Drug Antibody (ADA) assay development. Immobilized adalim*mab at 1 µg/ml, add increasing concentrations of Anti-Adalim*mab Antibodies (Cat. No. ADB-Y19, 10% human serum) and then add biotinylated adalim*mab at 5 µg/ml. Detection was performed using HRP-conjugated streptavidin with a sensitivity of 0.6 ng/mL.
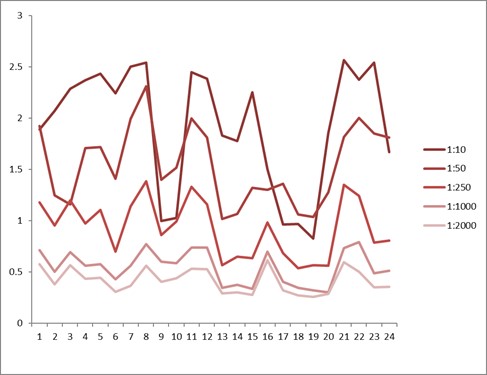
Comparison between anti-idiotypic capture ELISA and anti-idiotypic bridging ELISA for Ritux*mab detection in patient samples. Left: anti-idiotypic capture ELISA; Right: anti-idiotypic bridging ELISA.
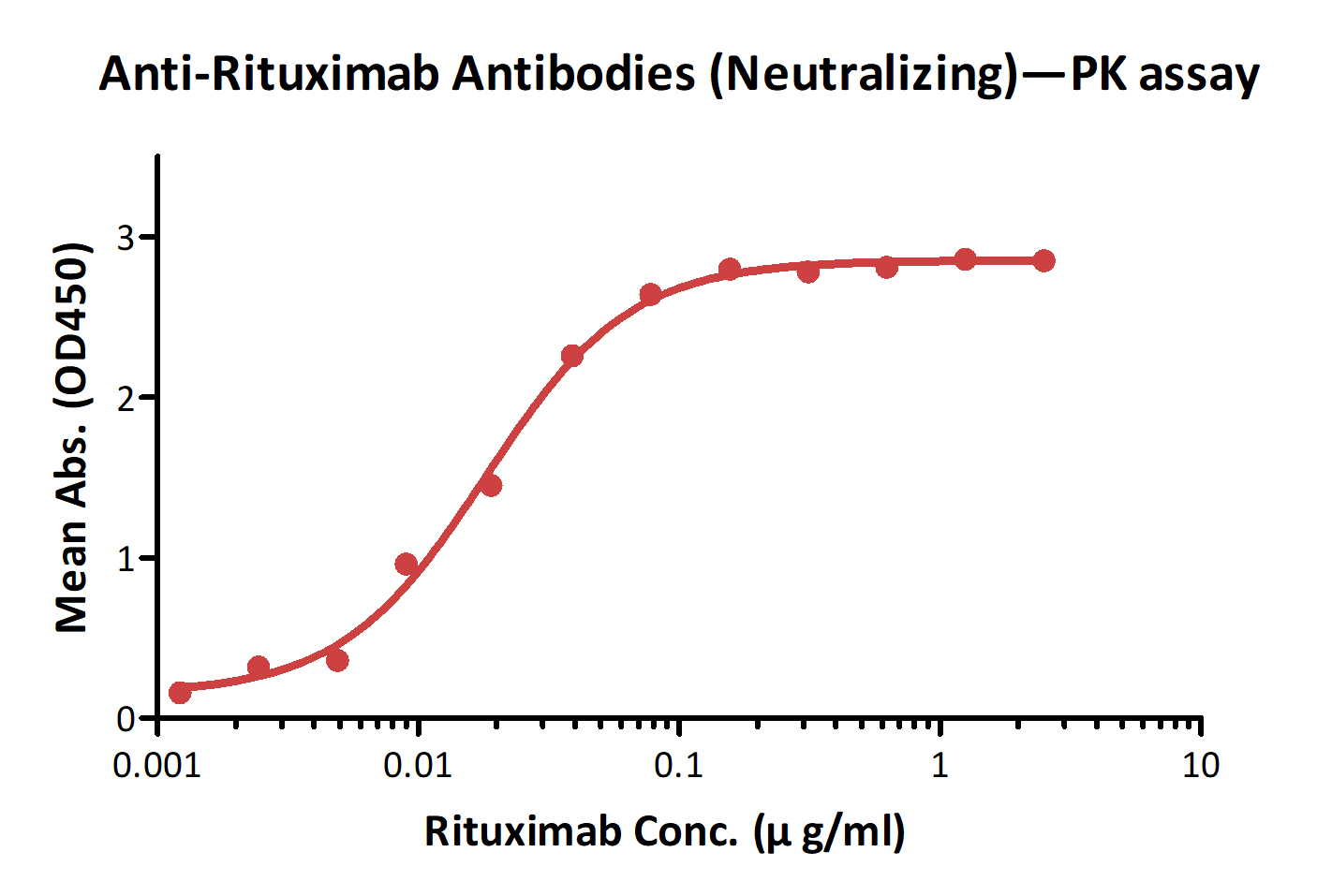
Detection of Ritux*mab by bridging ELISA in serum. Immobilized Anti-Ritux*mab Antibodies (Cat. No. RIB-Y37) at 2 μg/ml, added increasing concentrations of Ritux*mab (10% human serum) and then added biotinylated Anti-Ritux*mab Antibodies (Cat. No. RIB-BY35) at 1 μg/ml. Detection was performed using HRP-conjugated streptavidin with a sensitivity of 1 ng/ml.
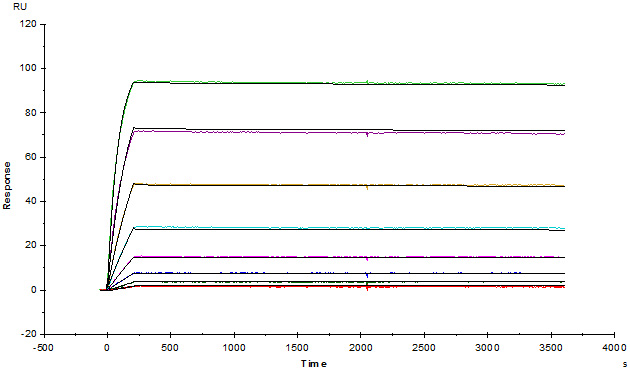
Anti-Adalim*mab Antibodies (mouse IgG1, Cat. No. ADB-Y19) captured on CM5 chip via anti-mouse antibodies surface, can bind human adalim*mab with an affinity constant of 1.36 pM.

Demonstration of the specificity of Anti-Cetux*mab Antibodies (Cat. No. CEB-Y28) to the Cetux*mab.
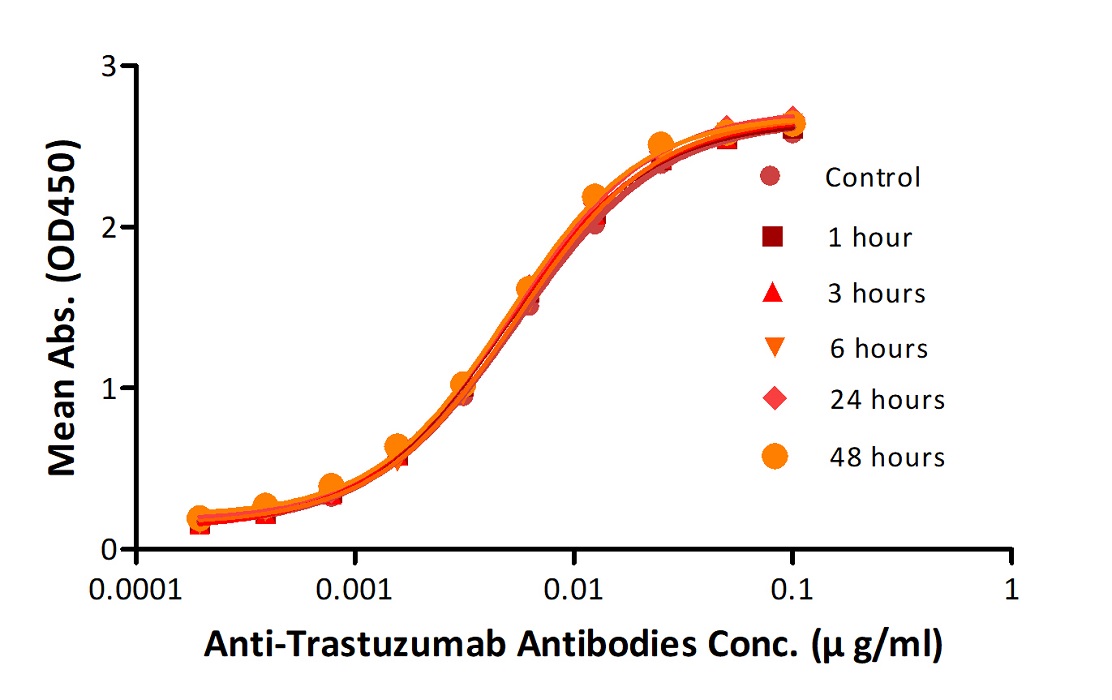
Reconstituted Anti-Trastuz*mab Antibodies were diluted to 0.4 mg/ml, aliquoted and placed at 37°C. Aliquots were removed from 37°C at every time point and placed at 4°C along with the control. No significant loss of activity was observed.
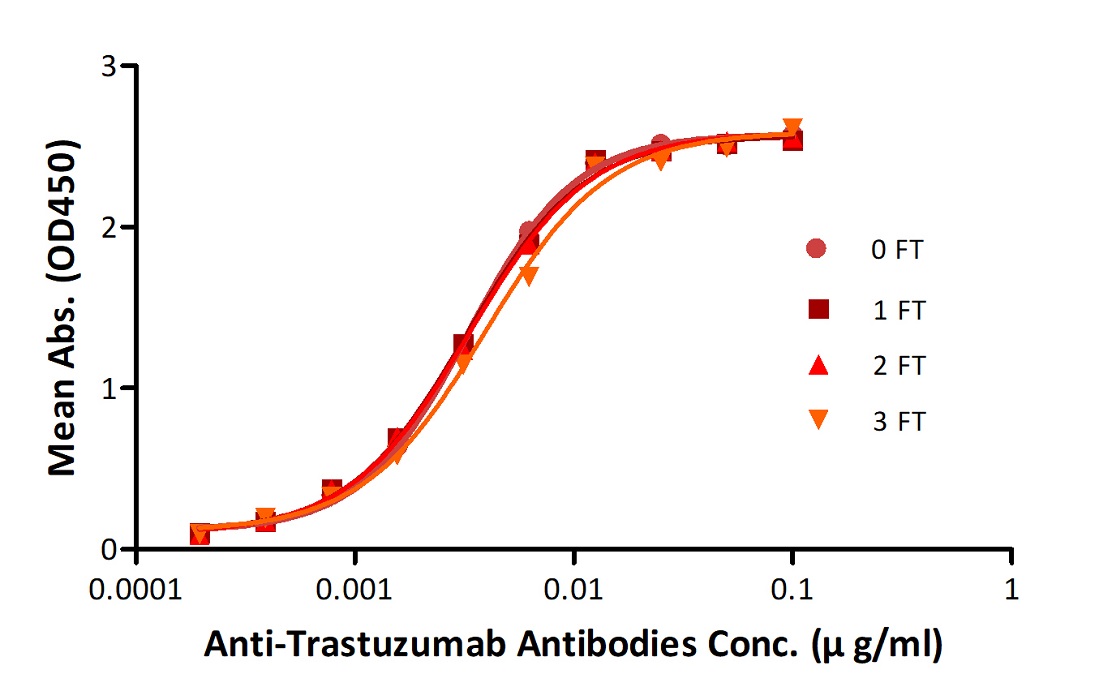
Anti-Trastuz*mab Antibodies were subjected to the indicated number of freeze-thaw cycles (FT). No significant loss of activity was observed.
This web search service is supported by Google Inc.
